6 Reasons Why Website Speed Matters & How Amazon Would Lose $1.6 Billion If It Slowed Down
How long do you wait for a website to load?
Well, according to statistics, half of us don’t even wait two seconds for website content to pop up!


That’s why I created the Bitcatcha speed checker. I wanted to make sure my server was reacting as fast as possible. And I want to help you test yours as well.
But, why is website load speed so important? What difference does a fraction of a second make?
The answer? It makes a big difference! It affects user experience, search rankings, and even sales and conversions.
1. Website speed is the first impression you ever make
First impressions are vital on the web.
Your customers, readers, and website visitors make an instant judgement about you and your business.
If your website loads fast, you’ve instantly made a strong first impression. It’s a quick-win for user experience! If it loads fast, your new visitor is immediately happy.
It’s pure psychology. We consider fast websites to be professional and reliable. We relate speed to efficiency, trust, and confidence.
“If it’s fast, it must be professional!”
A slow website, on the other hand, makes us think it’s unsafe, insecure, and untrustworthy. And it’s really difficult to turn around that negative first impression.
- 79% of online shoppers say they won’t go back to a website if they’ve had trouble with load speed.
You don’t get a second chance when it comes to user experience. Nearly 80% of your potential audience aren’t coming back.
2. We expect speed!
The internet sets a high bar when it comes to site speed. We expect, and demand fast loading times.
Here are the hard facts:
- 47% of people expect your site to load in less than 2 seconds.
- 40% will abandon it entirely if it takes longer than 3 seconds.
You get a little bit more room to move with mobile visitors, but not much.
- 85% of internet users expect a mobile site to load as fast or faster than on their desktop.
When we’re on the move, we tend to be even less patient. We want answers fast!


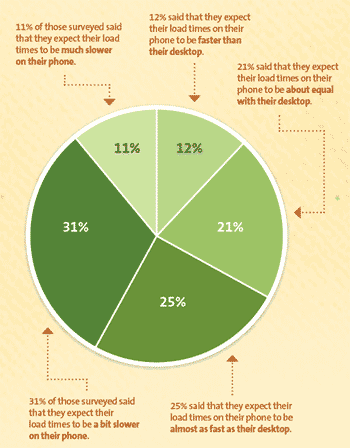

It’s clear that we all expect quick results whether we’re on a laptop, desktop, tablet, or mobile phone. Think about how you use the internet every day. You’re looking for quick answers and immediate results.
When it comes to well-known and authority sites, people are willing to wait a little longer. If you’re Google or Facebook, visitors will tolerate a small delay, because they’re an established name.
Unfortunately, for small businesses and startups, you don’t always have that luxury. It’s best to be as fast as possible right from the start.
3. User experience
I’ve written a lot about user experience and UX design. I think it’s one of the few ways that websites can really set themselves apart from the competition.
At it’s core, good UX design is all about creating a fantastic and simple experience for your visitors. There are two basic factors involved in a positive user experience:
- Give visitors what they’re looking for
- Give it to them fast.
That’s why website load speed is your number one priority when it comes to user experience. People visiting your website are looking for something. Give it to them as quickly as possible.
As soon as your visitors are confused or frustrated, you’ve done something wrong. And nothing frustrates us like a slow website!
4. Slow websites kills conversions
Let’s quickly revisit one of the first stats we showed you:
- 40% of people will abandon your site if it takes longer than 3 seconds to load.
Now, let’s say 100,000 people visit your site every month. If you slowed down to 4 seconds, you could lose 40,000 potential customers.
40,000!
If slow load speeds are driving people away, then it’s driving your sales away. This isn’t just speculation either. Some of the biggest companies on the planet have tested this out.
- Amazon did tests that showed they would lose $1.6 BILLION every year if they slowed down by just one second.
And Amazon are an established, recognisable company. If customers won’t wait just one extra second for Amazon, what chance have the rest of us got?
5. The long-term effect of slow website speed
We’ve established that slow loading speed leads to an instant drop-off in visitors. Nearly half of your potential visitors have already vanished. But there is a long-term effect here too. That long loading time gradually stunts your natural growth and word-of-mouth.
Customers slowly stop referring your service to others because of a poor experience. Established websites are less likely to link back to your content. It might even put people off signing up to your newsletter.
We often link a slow website to a lack of credibility, which may hurt your brand in the long run.
6. Website speed affects your Google rank
Google have a self-confessed love of speed.
“We’re striving to make the whole web fast”
They’re on a mission to make sure the internet is super speedy, easily accessible, and useful. So far, they’re doing a pretty good job.
There’s a lot of information out there about Google, load speed, and your search ranking. Some of it true, some of it not so much. Here’s what we know for sure from the mouths of Google themselves.
- Google do take website load speed into account when ranking websites (announced in 2010)
- But, it is a very small ‘signal’ (compared to relevance and authority)
“While site speed is a new signal, it doesn’t carry as much weight as the relevance of a page. Currently, fewer than 1% of search queries are affected by the site speed signal”
It basically means that the average websites won’t see much change. But, if your site is super slow, you will suffer.
But, here’s the interesting bit:
“Google will reduce the amount of crawlers it sends to your site if your server is slower than two seconds.”
That means Google is less likely to pick up your latest blog post, or notice any other recent updates. And that might harm you.
To make sure your server speed is up to standard, use our Bitcatcha server speed checker, and make sure your site measures up. If it’s less than two seconds, you might be effectively hiding yourself from Google’s crawlers.
Pro-tip : If your website is running on WordPress, be sure to check out these managed WordPress hosting because their services are well optimized for speed.
Speed matters. It affects your user experience, it it affects your search ranking. It affects your sales and conversions.
If you’re wondering how your server speed measures up, head over to our speed checker now, and compare your site against millions of others.
If you have any questions or thoughts on website load speed or server response times, please leave a comment below!







